

Dr. Parmar offers gastric band removal surgery for patients experiencing complications, insufficient weight loss, or who request removal after long-term use. This minimally invasive procedure is performed laparoscopically (keyhole surgery) under general anaesthesia. During the surgery, the entire gastric band, along with its tubing and skin port, is removed. The operation typically lasts 30 to 60 minutes, and most patients can return home the same day. Although the risk of complications—such as conversion to open surgery, wound infection, or injury to internal structures—is minimal, Dr. Parmar will thoroughly explain the procedure, risks, and expected outcomes during the consultation.
Gastric band surgery, also known as laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding (LAGB) or lap band surgery, is a weight-loss procedure designed to restrict food intake without permanently altering the stomach's anatomy.
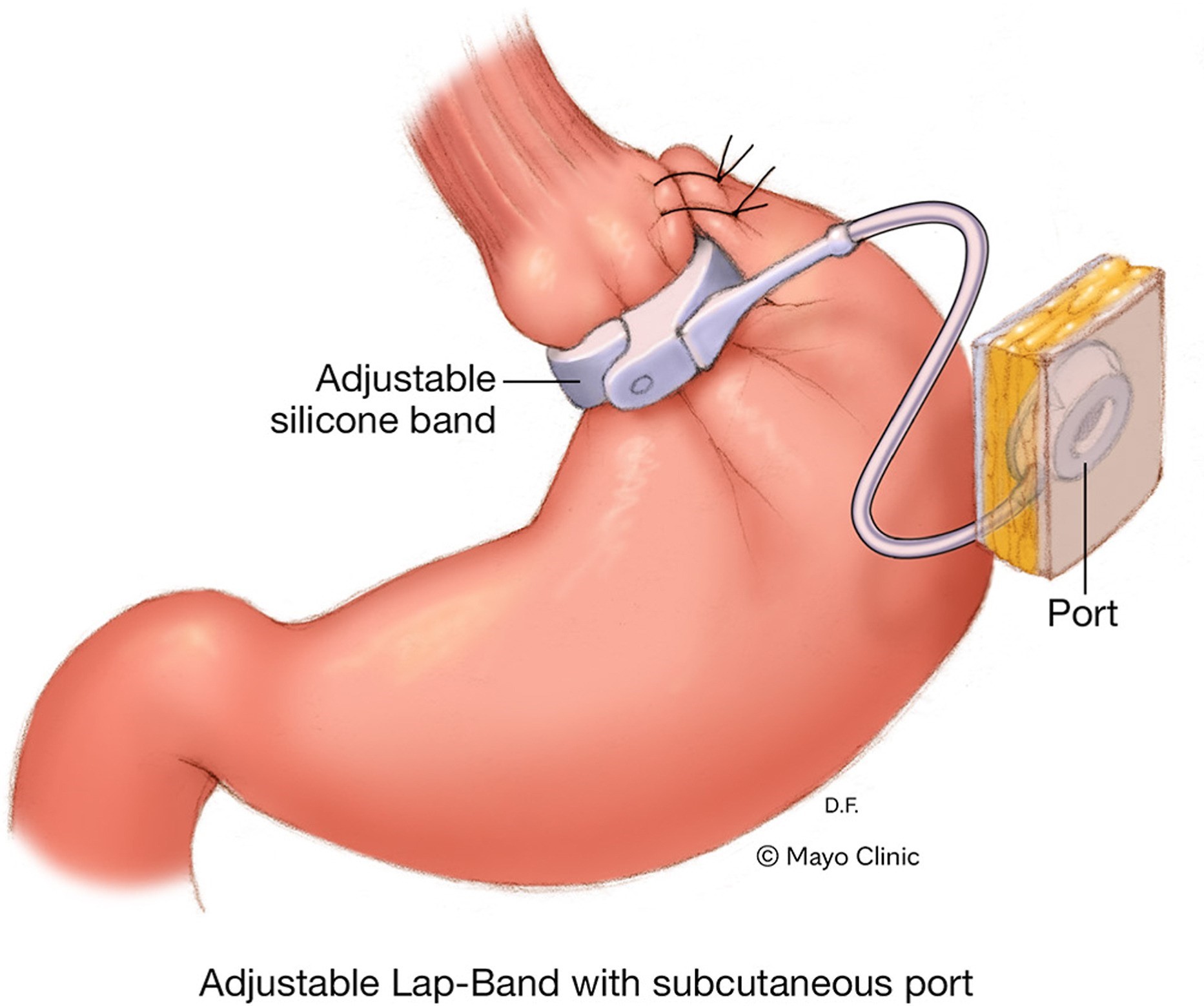
This minimally invasive keyhole surgery involves placing an inflatable silicone band around the upper part of the stomach. This creates a small pouch, limiting food intake and promoting a feeling of fullness after smaller meals. By reducing calorie consumption and prolonging satiety, the procedure supports effective and sustained weight loss.
The gastric band creates a small stomach pouch at the upper part of the stomach with a narrow opening to the rest of the stomach.
This procedure is typically recommended for individuals who:
As with any surgery, risks associated with general anaesthesia include wound infection, chest infection, deep vein thrombosis (DVT), or pulmonary embolism.
While the gastric band offers many benefits, there are significant long-term risks, with complication rates reported in up to 30 - 40% of patients. These include:
Due to the high rates of complications and the likelihood of future band removal, Dr. Parmar has discontinued offering gastric band surgery as a weight-loss solution.
Patients considering this procedure should be aware of the potential for follow-up surgeries and weigh the risks against the benefits of other bariatric options such as gastric bypass or sleeve gastrectomy.